Introduction to Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a crucial tool for organisations to identify and mitigate risks associated with data processing activities that may impact individuals’ privacy rights. In this expert guide, we’ll delve into the key principles of DPIAs and provide comprehensive guidance notes aligned with the laws of England and Wales.
Understanding the Purpose of DPIAs
Legal Framework
In England and Wales, DPIAs are a legal requirement under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for organisations processing personal data, particularly when undertaking high-risk data processing activities. Conducting a DPIA helps organisations comply with GDPR requirements and demonstrates accountability for data protection.
Risk Assessment
The primary purpose of a DPIA is to assess the potential risks to individuals’ privacy and data protection rights arising from data processing activities. By identifying and evaluating these risks, organisations can implement measures to mitigate or eliminate them, ensuring compliance with data protection laws and safeguarding individuals’ rights.
Key Components of DPIAs
Data Processing Activities
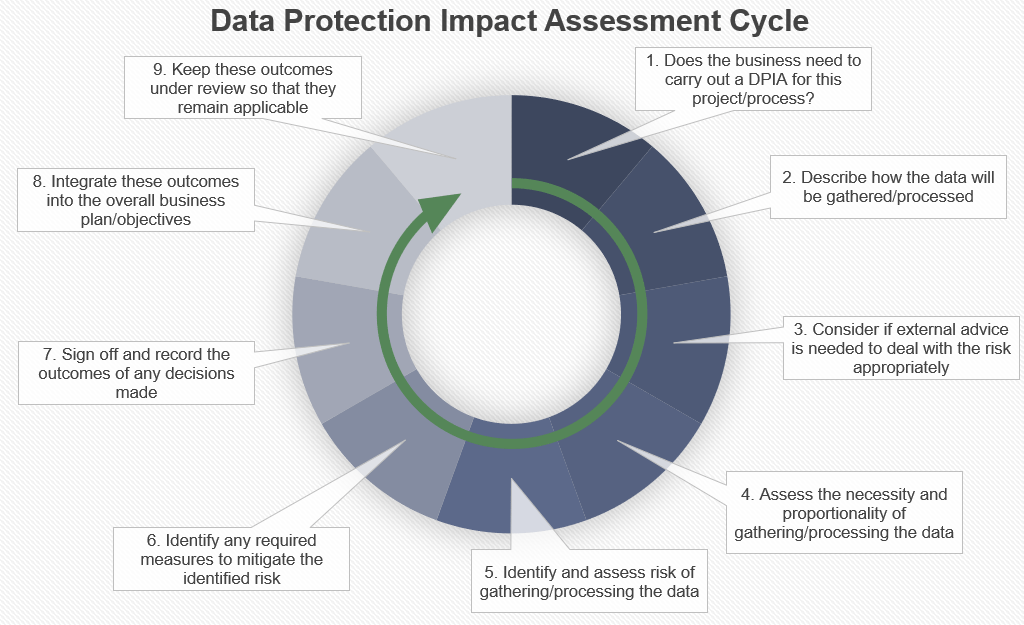
DPIAs should begin with a comprehensive inventory of data processing activities, including the types of personal data collected, the purposes of processing, and the parties involved. This step helps organisations gain a clear understanding of their data processing practices and identify potential risks to individuals’ privacy.
Risk Assessment Criteria
Organisations should assess the potential risks to individuals’ privacy and data protection rights using specific criteria outlined in GDPR guidelines. These criteria may include the nature, scope, context, and purposes of data processing, as well as the likelihood and severity of risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Conducting a DPIA
Data Protection Team
Organisations should establish a dedicated data protection team responsible for conducting DPIAs and ensuring compliance with data protection laws. This team may include data protection officers, legal advisors, IT specialists, and other relevant stakeholders with expertise in data privacy and security.
Stakeholder Engagement
Effective stakeholder engagement is essential throughout the DPIA process, involving input from key individuals, departments, and external partners affected by data processing activities. Collaboration ensures that all perspectives are considered, potential risks are identified, and appropriate measures are implemented to address them.
Mitigating Risks and Implementing Measures
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once potential risks have been identified through the DPIA process, organisations should implement appropriate measures to mitigate or eliminate these risks. This may include technical and organisational measures such as encryption, pseudonymisation, access controls, and staff training on data protection best practices.
Documentation and Reporting
Organisations must document the DPIA process, including the findings, risk assessments, and measures implemented to mitigate risks. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with GDPR requirements and may be subject to review by data protection authorities. Additionally, organisations should report significant risks and mitigation measures to relevant stakeholders and data protection authorities as required by law.
Conclusion: Ensuring Compliance and Protecting Individuals’ Rights
By following the DPIA guidance notes outlined in this expert guide, organisations in England and Wales can effectively identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with data processing activities, ensuring compliance with data protection laws and safeguarding individuals’ privacy rights. Conducting DPIAs demonstrates a commitment to accountability, transparency, and ethical data handling practices, fostering trust with stakeholders and enhancing data protection standards across organisations.
FAQs on Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) Guidance Notes
What is a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA), and why is it important?
A DPIA is a systematic process used to identify and mitigate risks associated with data processing activities that may impact individuals’ privacy rights. It is essential for organisations to conduct DPIAs to comply with data protection laws and ensure accountability for data processing practices.
When should organisations conduct a DPIA?
Organisations should conduct a DPIA before undertaking any data processing activities that are likely to result in high risks to individuals’ privacy and data protection rights. This includes the introduction of new systems or technologies, significant changes to existing processes, or processing activities involving sensitive personal data.
Who is responsible for conducting a DPIA within an organisation?
Organisations should designate a dedicated data protection team responsible for conducting DPIAs and ensuring compliance with data protection laws. This team may include data protection officers, legal advisors, IT specialists, and other relevant stakeholders with expertise in data privacy and security.
What are the key components of a DPIA?
Key components of a DPIA include identifying data processing activities, assessing potential risks to individuals’ privacy and data protection rights, implementing measures to mitigate or eliminate risks, and documenting the DPIA process and outcomes.
How should organisations assess the risks associated with data processing activities?
Organisations should assess risks using specific criteria outlined in GDPR guidelines, considering factors such as the nature, scope, context, and purposes of data processing, as well as the likelihood and severity of risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
What measures can organisations implement to mitigate risks identified in a DPIA?
Organisations can implement various measures to mitigate risks, including technical and organisational measures such as encryption, pseudonymisation, access controls, staff training, and regular monitoring and review of data processing activities.
Are there any specific requirements for documenting DPIA processes and outcomes?
Yes, organisations must document the DPIA process, including the findings, risk assessments, and measures implemented to mitigate risks. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance with GDPR requirements and may be subject to review by data protection authorities.
How often should organisations review and update DPIAs?
Organisations should review and update DPIAs regularly, particularly when significant changes occur in data processing activities or when new risks are identified. DPIAs should be revisited whenever there are changes in technology, legislation, or organisational practices that may impact data protection risks.
What are the consequences of failing to conduct a DPIA or address risks identified in a DPIA?
Failure to conduct a DPIA or address risks identified in a DPIA can result in non-compliance with data protection laws, potential fines, reputational damage, and loss of trust with stakeholders. Additionally, individuals may suffer harm or loss of privacy rights if risks are not adequately mitigated.
Where can organisations find additional guidance and support for conducting DPIAs?
Organisations can seek additional guidance and support for conducting DPIAs from data protection authorities, regulatory bodies, industry associations, and legal advisors specialising in data protection and privacy law. Additionally, online resources, training programmes, and professional networks may provide valuable insights and best practices for DPIA processes.
- Press Release – Product Update Announcement - July 19, 2024
- Press Release – New Service Announcement - July 19, 2024
- Press Release – Company Contract Award - July 18, 2024