Understanding DPIAs and Their Importance
DPIAs are systematic assessments of the potential impact of data processing activities on individuals’ privacy rights. They help organizations identify, assess, and mitigate privacy risks, ensuring compliance with data protection laws such as the Data Protection Act 2018 and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Legal Framework for DPIAs in the UK
DPIAs are a legal requirement under the GDPR for certain types of data processing activities, particularly those that are likely to result in high risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms. Organizations must conduct DPIAs whenever they engage in such processing activities, ensuring that privacy risks are adequately addressed.
Conducting a DPIA: Key Steps
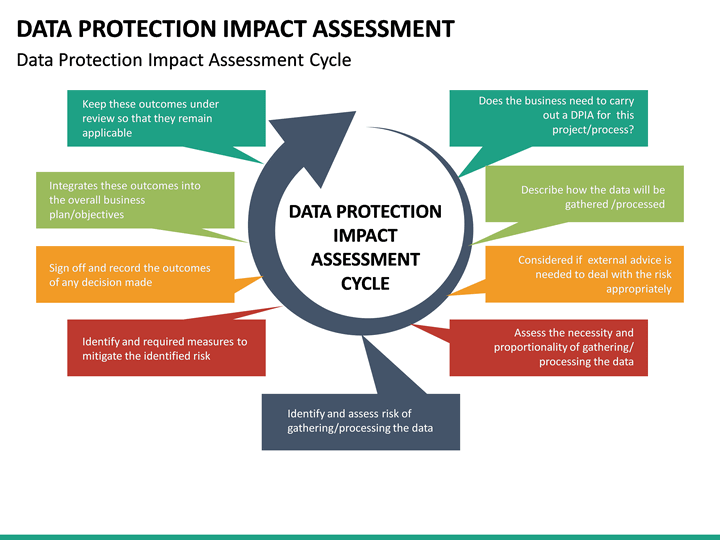
The DPIA process involves several key steps, including
- Identifying the need for a DPIA.
- Describing the data processing activity.
- Assessing the necessity and proportionality of the processing.
- Evaluating the potential impact on individuals’ privacy rights.
- Identifying and implementing measures to mitigate risks.
- Consulting with relevant stakeholders, including data subjects and data protection authorities.
Integrating DPIAs into Organizational Processes
DPIAs should be integrated into organizations’ data protection and risk management processes. This involves establishing DPIA policies and procedures, training staff members on DPIA requirements, and embedding DPIAs into project management processes to ensure that privacy risks are considered from the outset of new initiatives.
Documentation and Accountability
Organizations must document DPIA processes and decisions to demonstrate compliance with data protection laws and regulatory requirements. DPIA reports should include details of the data processing activity, the privacy risks identified, and the measures taken to mitigate those risks. This documentation helps organizations demonstrate accountability and transparency in their data processing practices.
Review and Continuous Improvement
DPIAs are not one-off exercises but should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in data processing activities, technology, and regulatory requirements. Organizations should establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and review of DPIA processes, ensuring that privacy risks are effectively managed over time.
Training and Awareness
Staff members involved in data processing activities should receive training and awareness programs on DPIA requirements and best practices. This helps ensure that DPIAs are conducted effectively and that staff members understand their roles and responsibilities in protecting individuals’ privacy rights.
Engaging with Data Subjects
DPIAs provide an opportunity for organizations to engage with data subjects and seek their input on the potential privacy risks associated with data processing activities. By involving data subjects in the DPIA process, organizations can demonstrate respect for individuals’ privacy rights and enhance trust and transparency.
Regulatory Oversight and Enforcement
Regulatory authorities have the power to review DPIAs and assess whether organizations have adequately addressed privacy risks in their data processing activities. Non-compliance with DPIA requirements can result in regulatory sanctions, including fines and enforcement actions, highlighting the importance of conducting DPIAs diligently and transparently.
Conclusion
DPIAs are essential tools for organizations to identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with data processing activities. By conducting DPIAs effectively and transparently, organizations can enhance data protection, build trust with stakeholders, and demonstrate compliance with data protection laws in the UK.
What is a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA), and when is it required?
A DPIA is a systematic process to identify and mitigate privacy risks in data processing activities. It is required under the GDPR for processing activities likely to result in high risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Who is responsible for conducting a DPIA within an organization?
DPIAs are typically conducted by data protection officers (DPOs) or individuals with data protection responsibilities within the organization. However, all individuals involved in data processing should be aware of DPIA requirements.
When should a DPIA be conducted during the data processing lifecycle?
DPIAs should ideally be conducted at the outset of a new project or data processing activity. However, they can also be conducted at any stage where significant changes are made to existing processing activities.
What are the key steps involved in conducting a DPIA?
Key steps in a DPIA include identifying the need for a DPIA, describing the data processing activity, assessing privacy risks, identifying and evaluating measures to mitigate risks, and documenting the DPIA process and outcomes.
How are privacy risks assessed in a DPIA?
Privacy risks are assessed based on factors such as the nature and scope of the processing activity, the types of personal data involved, the potential impact on individuals’ rights and freedoms, and the likelihood and severity of any harm.
What measures can be taken to mitigate privacy risks identified in a DPIA?
Mitigation measures may include implementing technical and organizational measures to enhance data security, limiting data collection and retention, providing transparency to data subjects, and conducting data protection training for staff.
Are there any templates or tools available to help conduct DPIAs?
Yes, there are various DPIA templates and tools available, including those provided by data protection authorities and industry associations. However, organizations may also develop their own customized DPIA templates based on their specific needs.
How long does it take to conduct a DPIA?
The time required to conduct a DPIA depends on factors such as the complexity of the processing activity, the availability of relevant information, and the level of stakeholder involvement. DPIAs should be conducted in a timely manner to ensure risks are identified and addressed promptly.
What happens if a DPIA identifies high risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms?
If a DPIA identifies high risks, organizations must take appropriate measures to mitigate those risks. In some cases, they may need to consult with data protection authorities or seek prior consultation with data subjects before proceeding with the processing activity.
Is a DPIA a one-time exercise, or should it be regularly reviewed and updated?
DPIAs are not one-time exercises but should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in data processing activities, technology, and regulatory requirements. Regular reviews ensure that privacy risks are effectively managed over time.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) Template
Introduction
- Provide an overview of the DPIA process and its purpose.
- Explain the legal requirements and obligations associated with conducting a DPIA.
Scope of Assessment
- Define the scope of the assessment, including the data processing activities and systems to be evaluated.
- Specify the objectives and goals of the DPIA.
Data Processing Activities
- Identify and describe the data processing activities involved.
- Document the types of personal data collected, processed, and stored.
Privacy Risks Assessment
- Assess potential privacy risks associated with the data processing activities.
- Evaluate the likelihood and severity of risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Risk Mitigation Measures
- Identify measures to mitigate identified privacy risks.
- Implement technical and organizational controls to enhance data protection.
Stakeholder Consultation
- Engage with relevant stakeholders, including data subjects, data protection officers, and legal advisors.
- Solicit feedback and input on privacy risks and mitigation measures.
Documentation and Reporting
- Document the DPIA process, findings, and outcomes.
- Prepare a DPIA report summarizing the assessment and recommendations.
Review and Approval
- Review the DPIA report with key stakeholders for approval.
- Obtain necessary approvals and sign-offs before implementing mitigation measures.
Implementation and Monitoring
- Implement approved mitigation measures and monitor their effectiveness.
- Establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring and review of data processing activities.
Review and Update
- Schedule regular reviews and updates of the DPIA to reflect changes in data processing activities, technology, and regulatory requirements.
- Ensure that the DPIA remains relevant and effective over time.
Conclusion
- Summarize key findings and recommendations from the DPIA.
- Emphasize the importance of ongoing compliance with data protection laws and regulations.
- Press Release – Product Update Announcement - July 19, 2024
- Press Release – New Service Announcement - July 19, 2024
- Press Release – Company Contract Award - July 18, 2024