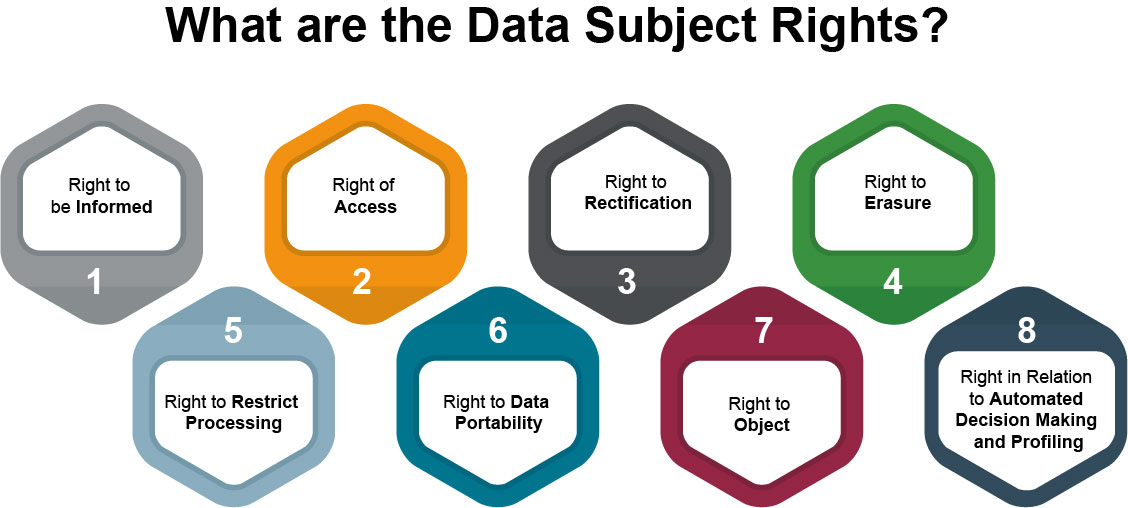
What are Data Subject Rights?
Data Subject Rights refer to the rights individuals have over their personal data. These rights include the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, data portability, object to processing, and not be subject to automated decision-making.
Why is a Data Subject Rights Policy important?
A Data Subject Rights Policy outlines how organisations handle requests from individuals exercising their rights under data protection laws. It ensures transparency, accountability, and compliance with legal obligations regarding personal data.
Key Elements of a Data Subject Rights Policy
Right to Access
Organisations must provide individuals with access to their personal data upon request. The policy should detail how requests are made, processed, and responded to within the statutory timeframe of one month.
Right to Rectification
Individuals have the right to request the correction of inaccurate or incomplete personal data. The policy should outline procedures for handling rectification requests promptly and effectively.
Right to Erasure (Right to be Forgotten)
Organisations must delete personal data upon request if there is no legitimate reason for its continued processing. The policy should specify when erasure applies and any exceptions under data protection laws.
Right to Restrict Processing
Individuals can request the restriction of processing their personal data under certain circumstances. The policy should explain how such requests are assessed and implemented by the organisation.
Right to Data Portability
Individuals have the right to receive their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. The policy should detail procedures for providing data portability upon request.
Right to Object to Processing
Individuals can object to the processing of their personal data, including for direct marketing purposes. The policy should outline how objections are handled and the organisation’s obligations in responding to such requests.
Rights in Relation to Automated Decision Making and Profiling
Organisations must inform individuals if decisions are made solely based on automated processing, including profiling. The policy should describe how individuals can request human intervention and challenge automated decisions.
Implementing the Data Subject Rights Policy
Legal Compliance and Accountability
Organisations must ensure their Data Subject Rights Policy aligns with UK data protection laws, including the DPA 2018 and GDPR. This involves training staff, maintaining records of processing activities, and cooperating with regulatory authorities.
Conclusion
A well-defined Data Subject Rights Policy is essential for organisations to uphold individuals’ rights and comply with UK data protection legislation effectively. By implementing transparent procedures and respecting data subject rights, organisations build trust and ensure responsible data management practices.
What is a Data Subject Rights Policy?
A Data Subject Rights Policy outlines how organisations handle individuals’ requests to exercise their rights over their personal data under data protection laws, such as the GDPR and Data Protection Act 2018.
What rights are covered under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
It typically covers rights such as the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, data portability, object to processing, and not be subject to automated decision-making.
How can I request access to my personal data under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
You can request access to your personal data by submitting a Subject Access Request (SAR) to the organisation. The policy should outline how to make such requests and the organisation’s process for responding.
What should I do if my personal data is inaccurate or incomplete?
If you believe your personal data is inaccurate or incomplete, you have the right to request rectification. The Data Subject Rights Policy should detail how to request rectification and the organisation’s procedures for correcting data.
Can I request the deletion of my personal data under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
Yes, you have the right to request the erasure of your personal data, also known as the right to be forgotten, under certain circumstances. The policy should explain when erasure applies and any exceptions to this right.
How does a Data Subject Rights Policy handle restrictions on processing personal data?
If you wish to restrict the processing of your personal data, you can request this under specific conditions outlined in the policy. The organisation should detail how it assesses and implements such requests.
What is data portability, and how does it work under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
Data portability allows you to receive your personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format. The policy should describe how to request data portability and how the organisation facilitates this process.
Can I object to the processing of my personal data under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
Yes, you have the right to object to the processing of your personal data, including for direct marketing purposes. The policy should clarify how to submit objections and how the organisation handles such requests.
What rights do I have regarding automated decision-making and profiling under a Data Subject Rights Policy?
You have the right to be informed if decisions are made solely based on automated processing, including profiling. The policy should explain how you can request human intervention and challenge automated decisions.
How does a Data Subject Rights Policy ensure compliance with data protection laws?
A Data Subject Rights Policy ensures compliance by outlining procedures that align with UK data protection laws, educating staff, maintaining records of processing activities, and cooperating with regulatory authorities like the ICO.
- Short Memorandum Of Understanding For Commercial Transactions - August 8, 2024
- Privacy Notice Templates - August 7, 2024
- Paid Business Directory Website Terms Of Use - August 7, 2024